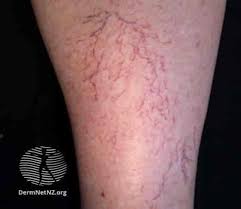
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins that commonly appear on the legs. They occur when the valves in the veins weaken or become damaged, leading to blood pooling and increased pressure within the affected veins. Varicose veins can be unsightly and may cause discomfort, pain, or other symptoms.
This can be due to a variety of factors, including genetics, age, pregnancy, and obesity. Other risk factors include being female, having a job that requires long periods of standing or sitting, and having a history of blood clots.
Causes of Varicose Veins
- Weak or damaged valves in the veins: Valves in the veins help regulate blood flow by preventing the backward flow of blood. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can pool in the veins, leading to varicose veins.
- Age: The risk of developing varicose veins increases with age as the veins lose their elasticity and valves become less efficient.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, and the use of hormonal birth control methods.
- Family history: A family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Prolonged standing or sitting: Occupations or activities that involve long periods of standing or sitting can increase the risk of developing varicose veins.
Pregnancy is also a common cause of varicose veins, as the growing uterus puts pressure on the veins in the pelvis and legs.
Finally, obesity is another risk factor for varicose veins, as excess weight can put added pressure on the veins and make it harder for blood to flow properly.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins can cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Pain, swelling, and discoloration are some of the most common symptoms associated with varicose veins.
- Dark purple or blue veins that appear twisted and bulging on the skin’s surface. Discoloration is another common symptom of varicose veins, and it can manifest as a darkening or reddening of the skin around the affected veins.
- The pain can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation, and it is often described as a Aching, throbbing, or heaviness in the legs.
- Swelling, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.The pain can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation, and it is often described as a
- Itching or irritated skin around the affected veins.
- Muscle cramps or a feeling of restlessness in the legs.
- Discomfort worsened by prolonged sitting or standing.
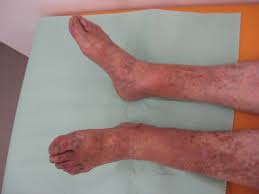
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
There are several treatment options available for varicose veins, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, elevating the legs, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and wearing compression stockings can help alleviate symptoms and prevent varicose veins from worsening.
- Sclerotherapy: This procedure involves injecting a solution directly into the affected veins, causing them to scar and close.
- Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT): A laser fiber is inserted into the affected vein, delivering laser energy that causes the vein to collapse and seal shut.
- Vein stripping: In more severe cases, the affected vein may be surgically removed through small incisions.
- Endoscopic vein surgery: This procedure is used for treating advanced cases of varicose veins and involves using a thin camera (endoscope) to visualize and remove veins through small incisions.
- Laser or radiofrequency ablation: Similar to EVLT, these treatments use laser or radiofrequency energy to close off the affected vein.
Compression stockings can also be worn to help improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs.
Medical procedures such as sclerotherapy, laser treatment, and vein stripping may be recommended for more severe cases. These procedures are generally safe and effective, but they do carry some risks and potential side effects. It is important to discuss the pros and cons of each treatment option with your doctor to determine which one is right for you.
Prevention of Varicose Veins
FOODS THAT HELP FOR VARICOSE VEINS:
- High-fiber foods: Consuming a diet rich in fiber can help prevent constipation, which can contribute to varicose veins. Include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts in your meals.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Antioxidants help protect the blood vessels from damage caused by free radicals. Include foods such as berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, bell peppers, and tomatoes, which are rich in antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and flavonoids.
- Foods rich in flavonoids: Flavonoids have been shown to improve blood circulation and strengthen blood vessels. Include foods such as onions, garlic, citrus fruits, berries, dark chocolate, and green tea, which are rich in flavonoids.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties and may help improve blood circulation. Include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your diet.
- Potassium-rich foods: Potassium helps maintain proper fluid balance in the body and may reduce water retention, which can contribute to swelling. Include foods such as bananas, avocados, sweet potatoes, spinach, and tomatoes, which are good sources of potassium.
- Garlic and onions: These foods have natural anti-inflammatory properties and can help improve blood circulation. Incorporate them into your meals for added benefits.
- Water: Staying hydrated is important for overall vascular health. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to maintain proper hydration.
Regular exercise is one of the best ways to prevent varicose veins. By keeping your legs moving, you can improve circulation and reduce the risk of blood pooling in your veins. Try to incorporate activities like walking, cycling, or swimming into your daily routine.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also important for preventing varicose veins. Excess weight puts added pressure on your veins, which can lead to damage over time. Eating a balanced diet and staying active can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce your risk of developing varicose veins.
DIAGNOSING FACTORS :
When it comes to varicose veins, a physical examination by a healthcare professional is usually sufficient for diagnosis. They will typically evaluate your symptoms and visually examine the affected veins. However, in certain cases, additional tests may be recommended to assess the severity of the condition and plan appropriate treatment. Here are some tests that may be used:
- Doppler ultrasound: This is the most common test for varicose veins. It uses sound waves to create images of the veins and assess blood flow. Doppler ultrasound can help identify any underlying venous insufficiency, blood clots, or other abnormalities.
- Venogram: In this procedure, a dye is injected into the veins, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the veins and blood flow. Venograms are typically used in more complex cases or when other tests are inconclusive.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) scan: These imaging tests may be used in specific situations to get detailed images of the veins and surrounding structures.
Living with Varicose Veins
Living with varicose veins can be challenging, but there are many ways to manage the symptoms and improve your quality of life. One important aspect of self-care is maintaining a healthy weight, as excess weight can put extra pressure on your veins and worsen the condition. Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can also help improve circulation and reduce swelling.
In addition to lifestyle changes, there are various medical treatments available for varicose veins, such as sclerotherapy and laser therapy. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your individual needs. Lastly, it’s essential to prioritize self-care and seek support from loved ones and healthcare professionals when needed.
COMPLICATIONS OF VARICOSE VEINS
Varicose veins can sometimes lead to complications, which may include:
- Ulcers: In some cases, varicose veins can cause skin ulcers, especially around the ankles. These ulcers can be painful and slow to heal. They are typically a result of long-term venous insufficiency, which leads to poor circulation and tissue damage.
- Blood clots: Varicose veins increase the risk of developing blood clots, particularly deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Blood clots can be dangerous if they travel to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, causing a potentially life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism.
- Bleeding: Bulging varicose veins close to the skin surface are more prone to injury. Even minor trauma or scratching can cause them to bleed profusely. While the bleeding is usually not severe, it can be alarming and require medical attention.
- Superficial thrombophlebitis: This refers to the inflammation of a superficial vein due to a blood clot. It typically causes pain, redness, and swelling along the affected vein. Although it is not usually a severe condition, it may require medical treatment.
- Hyperpigmentation and skin changes: Varicose veins can cause changes in the skin, such as darkening or discoloration (hyperpigmentation). The affected skin may become dry, itchy, and prone to rashes or dermatitis.
- Spontaneous bleeding: In rare cases, varicose veins may rupture spontaneously, resulting in significant bleeding. This typically occurs in large, untreated varicose veins.
- Ankle swelling and discomfort: Varicose veins can cause chronic swelling in the ankles, leading to discomfort, heaviness, and aching sensations.