INTRODUCTION:
The human body is a remarkable and complex system composed of various interconnected networks. While most of us are familiar with major bodily systems such as the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, there is one lesser-known system that plays a vital role in maintaining our health and defending us against diseases—the lymphatic system. Often overshadowed by its more prominent counterparts, the lymphatic system is a crucial component of our immune defense and overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the lymphatic system, exploring its structure, functions, and significance in maintaining a healthy immune response.
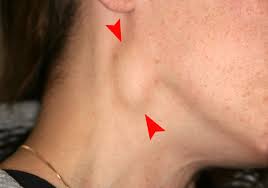
WHAT IS LYMPHADENOPATHY:
Lymphadenopathy occurs when lymph nodes become enlarged, typically due to the accumulation of immune cells and fluid. Lymph nodes are present throughout the body, particularly in the neck, armpits, groin, and behind the ears. They play a vital role in the immune system’s response to infections, cancer, and other diseases.
CAUSES OF LYMPHADENOPATHY:
Lymphadenopathy can be caused by various factors, including:
- Infections: Most commonly, lymphadenopathy is a result of an infection. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections such as strep throat, mononucleosis, tuberculosis, or HIV can trigger the enlargement of lymph nodes.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Certain inflammatory disorders, like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, can lead to lymphadenopathy.
- Immune System Disorders: Autoimmune diseases such as Hodgkin’s lymphoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) can cause lymphadenopathy.
- Cancer: Lymphadenopathy can be an early sign of cancer. It may occur when cancer cells from the original site spread to nearby lymph nodes or if lymphomas develop within the nodes themselves.
SYMPTOMS INCLUDE :
The primary symptom of lymphadenopathy is the presence of enlarged lymph nodes. Other accompanying signs and symptoms may include:
- Swelling or lumps in the affected area (neck, armpits, groin).
- Tenderness or pain in the swollen lymph nodes.
- Redness or warmth over the affected area.
- Fever or night sweats.
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss (in cases of cancer).
- Additional symptoms related to the underlying cause (e.g., sore throat, skin rashes, etc.).
DIAGNOSING FACTORS OF LYMPHADENOPATHY:
When diagnosing lymphadenopathy, healthcare professionals consider various factors to determine the underlying cause. Here are some key factors that play a role in diagnosing lymphadenopathy:
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the patient’s medical history, including any recent infections, illnesses, or surgeries. They will also ask about symptoms and their duration, previous exposure to risk factors, and any relevant family history.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is conducted to assess the size, location, and characteristics of the enlarged lymph nodes. The healthcare provider will palpate (feel) the lymph nodes to check for tenderness, consistency, and mobility. They may also examine other parts of the body for additional signs and symptoms.
- Lymph Node Characteristics: The specific features of the enlarged lymph nodes are carefully evaluated. This includes noting the size, shape, and consistency of the nodes. For example, lymph nodes associated with infections are typically soft and tender, while those related to cancer may be hard and fixed.
- Associated Symptoms: The presence of accompanying symptoms is crucial in determining the underlying cause of lymphadenopathy. Symptoms such as fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, sore throat, skin rashes, or joint pain can provide valuable clues.
- Blood Tests: Various blood tests may be ordered to assess the overall health and check for specific infections or markers associated with autoimmune disorders or cancer. These tests may include a complete blood count (CBC), inflammatory markers (e.g., C-reactive protein), viral serology, or specific antibodies.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT scan), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be employed to visualize the lymph nodes and surrounding structures. These tests help evaluate the size, shape, and internal characteristics of the nodes, providing additional information for diagnosis.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy of the enlarged lymph node may be required to determine the cause definitively. A small sample of the node is removed and analyzed under a microscope. The biopsy can help identify infections, inflammation, or cancerous cells, guiding further treatment decisions.
It is important to note that the specific diagnostic approach may vary depending on the individual case and the suspected underlying cause. The healthcare provider will tailor the diagnostic process based on the patient’s unique presentation and medical history.
TREATMENT :
The treatment of lymphadenopathy depends on the underlying cause. If an infection is present, antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal drugs may be prescribed. In cases of autoimmune disorders, treatment focuses on managing the underlying condition with immunosuppressive medications. For cancer-related lymphadenopathy, treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies.
When to Seek Medical Attention:While lymphadenopathy is often benign and resolves on its own, certain situations warrant prompt medical attention. These include:
- Persistent or progressively worsening swelling of lymph nodes.
- Enlarged lymph nodes accompanied by severe pain or other concerning symptoms.
- Enlarged lymph nodes that persist for more than two weeks.
- Lymphadenopathy in children or infants.
- Generalized swelling of lymph nodes throughout the body.
CONCLUSION:
Lymphadenopathy is a common condition characterized by the enlargement of lymph nodes. While it can be a response to an infection or inflammation, it can also indicate more serious underlying conditions, including cancer. Prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the cause and appropriate treatment. If you notice persistent or concerning lymph node enlargement, it is advisable to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and management.