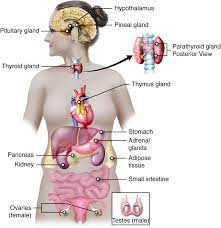
1.FEMALE HORMONES
Females produce a variety of hormones that play crucial roles in their overall health, reproductive system, and development. Here are some of the key hormones in females:
- Estrogen: Estrogen is the primary female sex hormone and plays a vital role in the development and regulation of the female reproductive system. It promotes the growth and development of the breasts, regulates the menstrual cycle, and contributes to the maintenance of bone health.
- Progesterone: Progesterone is another important female sex hormone. It is primarily involved in preparing the uterus for pregnancy and maintaining pregnancy. It helps regulate the menstrual cycle and supports the growth and development of the uterine lining.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): FSH is produced by the pituitary gland and plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle. It stimulates the growth and development of ovarian follicles, which contain eggs, and promotes the production of estrogen.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): LH is also produced by the pituitary gland and works in conjunction with FSH. It triggers ovulation, the release of a mature egg from the ovary, and stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine gland formed after ovulation.
- Prolactin: Prolactin is primarily known for its role in lactation and milk production. It is produced by the pituitary gland and helps stimulate the growth of breast tissue and the production of milk during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Thyroid hormones: While both males and females have thyroid hormones, they are particularly important for females due to their impact on the menstrual cycle and overall reproductive health. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism and energy levels and help maintain the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
These are just a few examples of the hormones that play essential roles in females. Hormones work in harmony, and any imbalance can have various effects on a woman’s health and well-being. It’s important to note that individual hormone levels can vary depending on factors such as age, menstrual cycle phase, pregnancy, and underlying health conditions.
2.FOODS TO BE TAKEN
Certain foods can have an impact on female hormones by either promoting hormonal balance or causing hormonal fluctuations. It’s important to note that while some foods may influence hormone levels, the effects may vary from person to person. Here are some foods that are believed to affect female hormones:
Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are rich in lignans, which are phytoestrogens that can mimic estrogen in the body. They may help balance estrogen levels and reduce the risk of estrogen-related conditions.

Soy: Soy contains isoflavones, another type of phytoestrogen. These compounds can interact with estrogen receptors in the body, potentially reducing symptoms of menopause and supporting hormonal balance.

Cruciferous vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and Brussels sprouts contain indole-3-carbinol, a compound that supports estrogen metabolism. It helps the liver metabolize estrogen more efficiently and may reduce the risk of estrogen-related cancers.

Wild-caught fatty fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation in the body. They may also support hormone production and balance.

Berries: Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially supporting hormone balance.

Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties. It may help regulate hormone levels and reduce symptoms related to hormone imbalances.

Dark chocolate: Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content contains flavonoids that can support cardiovascular health and reduce stress. It may also have a positive impact on mood and hormone balance.

Green tea: Green tea contains antioxidants and compounds like catechins, which may have an influence on hormone metabolism. It’s believed to support weight management and hormonal health.

It’s important to maintain a balanced and varied diet that includes a wide range of nutrients to support overall health and hormonal balance. If you have specific concerns about your hormone levels or any related conditions, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
3.FRESH JUICES
WHICH ARE PACKED WITH NATURAL ANTIOXIDANTS HELP US TO REGULATE HORMONES IN A BALANCED STATE
ABC juice(APPLE,BEETROOT,CARROT):ABC juice is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Apples provide vitamins A, C, and E, along with fiber. Beetroot is rich in iron, folate, and potassium. Carrots are a good source of beta-carotene, vitamin K, and potassium. Consuming ABC juice can help ensure a diverse range of nutrients in your diet.This can help kickstart your day and improve alertness and productivity.

Ash gourd juice: acts as hydrating ,detoxifying and natural coolant that reduces inflammation in the gastro intestinal tract. It is rich in vitamin c and B-complex and minerals like iron ,potassium and calcium. Acts on urinary system

Amla juice:Amla is one of the richest sources of vitamin C, containing significantly more vitamin C than citrus fruits. Consuming amla juice on an empty stomach can help boost your daily vitamin C intake, which supports immune function, collagen synthesis, and antioxidant activity.Amla is known for its benefits to hair and skin. The vitamin C and antioxidants present in amla juice help nourish the scalp, promote hair growth, and strengthen hair follicles.Amla juice may help regulate blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin secretion and improving glucose metabolism. Drinking it on an empty stomach may have a positive impact on blood sugar control.

4.FOODS TO BE AVOIDED :
Some foods can potentially cause hormonal fluctuations in the body. However, it’s important to note that the effects may vary from person to person and may not have significant impacts in most cases. Here are some foods that are often associated with potential hormonal fluctuations:
High-glycemic index carbohydrates: Foods with a high glycemic index, such as refined grains, sugary snacks, and processed carbohydrates, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This can lead to a surge in insulin production, potentially affecting other hormones in the body.
Caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can affect the central nervous system and may influence hormone levels. It can temporarily increase cortisol, the stress hormone, and affect sleep patterns, which can indirectly impact other hormonal functions.

Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt hormone balance. It may increase estrogen levels and decrease testosterone production, leading to hormonal imbalances in the long term.

High-fat foods: Consuming high-fat foods, particularly those high in saturated and trans fats, may contribute to weight gain and obesity. Excess body fat can promote estrogen production and disrupt hormone balance.

Soy in large amounts: While moderate amounts of soy products can be beneficial due to their phytoestrogen content, excessive consumption of soy or soy-based products may interfere with hormone regulation in some individuals.
Artificial sweeteners: Some studies suggest that certain artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame and sucralose, may have the potential to disrupt hormonal signaling. However, more research is needed to fully understand their effects on hormone levels.

Dairy products: Some studies have suggested that dairy products, particularly those from conventionally raised cows, may contain hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. However, the impact of these hormones on human health and hormone levels is still a subject of debate.