INTRODUCTION:
Endometriosis is a chronic and often debilitating condition that affects millions of women worldwide. Despite its prevalence, there is still a lack of awareness and understanding surrounding this condition.
WHAT IS ENDOMETRIOSIS?
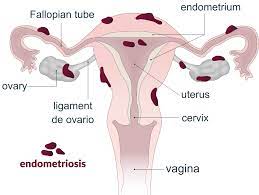
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that typically lines the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. This abnormal growth can occur in various areas, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic cavity, and even other distant organs like the lungs or bladder. These misplaced tissues still respond to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, leading to inflammation, pain, and the formation of scar tissue.
CAUSES OF ENDOMETRIOSIS:
While the exact cause of endometriosis remains unknown, several theories attempt to explain its origin. These theories include retrograde menstruation, where menstrual blood containing endometrial cells flows backward into the pelvic cavity, genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors.
SYMPTOMS OF ENDOMETRIOSIS:
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary from mild to severe, and some women may even be asymptomatic. Common symptoms include:
- Pelvic pain: Chronic pelvic pain, especially during menstruation, is one of the hallmark symptoms of endometriosis. The pain may also be present during intercourse or bowel movements.
- Heavy or irregular periods: Women with endometriosis often experience abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, as well as irregular menstrual cycles.
- Infertility: Endometriosis can affect fertility, making it more challenging for women to conceive. Approximately 30-50% of women with endometriosis may experience difficulties getting pregnant.
- Fatigue and gastrointestinal issues: Some women may experience fatigue, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, or other gastrointestinal symptoms due to endometriosis.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing endometriosis can be challenging, as its symptoms can overlap with other conditions. However, if endometriosis is suspected, various diagnostic methods can be employed, including medical history evaluation, pelvic exams, ultrasound imaging, and laparoscopy, which is considered the gold standard for definitive diagnosis.
Diagnosing endometriosis can be challenging due to the variability of symptoms and the fact that they can overlap with other conditions. However, healthcare professionals consider several factors when evaluating a patient for endometriosis. Here are some of the key diagnosing factors:
- Medical History: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history is essential. This includes discussing the nature, severity, and duration of symptoms, as well as any relevant family history of endometriosis or other reproductive disorders.
- Pelvic Examination: During a pelvic exam, a healthcare provider may manually palpate the pelvic area to check for abnormalities, such as cysts or nodules. However, it’s important to note that endometriosis lesions are not always palpable, and the absence of physical findings does not rule out the condition.
- Symptom Assessment: A detailed assessment of the patient’s symptoms is crucial. Common symptoms associated with endometriosis include pelvic pain, painful periods, pain during intercourse, heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, gastrointestinal issues, and infertility. The presence and severity of these symptoms can provide important clues for diagnosis.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be used to visualize the pelvic area and identify potential endometriotic cysts or other abnormalities. However, these imaging studies cannot definitively confirm the presence of endometriosis and are often used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods.
- Laparoscopy: Laparoscopy is considered the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis. It is a surgical procedure in which a small camera is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen, allowing the healthcare provider to directly visualize the pelvic organs. During laparoscopy, the surgeon can identify and biopsy any suspicious lesions or adhesions for confirmation of endometriosis.
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms does not always correlate with the extent of endometriosis. Some women with minimal symptoms may have extensive endometriosis, while others with severe symptoms may have milder forms of the condition. Thus, a comprehensive evaluation, including a combination of medical history, symptom assessment, physical examination, and possibly laparoscopy, is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
If you suspect you may have endometriosis or are experiencing symptoms suggestive of the condition, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in women’s health or gynecology. They can conduct a thorough evaluation and guide you through the diagnosis process.
TREATMENT:
The treatment options for endometriosis depend on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s desire for fertility. They may include:
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain associated with endometriosis.
- Hormonal therapy: Hormonal medications, such as birth control pills, progestins, or GnRH agonists, can help regulate hormonal imbalances and reduce symptoms.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery can be performed to remove endometrial implants, scar tissue, or cysts. In severe cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended.
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): In cases where fertility is affected, procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be employed to increase the chances of conception.
CONCLUSION:
Endometriosis is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects many women worldwide. By raising awareness and promoting early diagnosis, we can help alleviate the suffering associated with endometriosis and improve the quality of life for those affected. If you suspect you may have endometriosis or experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and guide you toward appropriate treatment options. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you manage and overcome the challenges of endometriosis.