Introduction
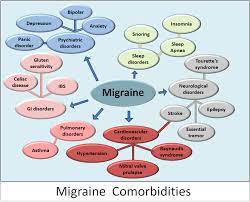
Migraines are more than just a headache. They can be debilitating, affecting every aspect of a person’s life. From their ability to work to their social interactions, migraines have a way of taking over. In fact, according to recent studies, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world.
But what exactly is a migraine? It’s not just a throbbing pain in your head. Migraine symptoms can include sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, vomiting, and even visual disturbances. It’s a complex neurological condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
What is a Migraine?
A migraine is a neurological condition that causes severe, recurring headaches. Unlike a regular headache, migraines are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Migraine attacks can last anywhere from a few hours to several days, and they can be debilitating for those who suffer from them.
The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to changes in the brain and nervous system. Some triggers that can bring on a migraine include stress, certain foods, hormonal changes, and environmental factors. It’s important to note that everyone’s experience with migraines is different, so it’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan for you.
Causes of Migraine
One of the primary causes of migraines is genetics. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of migraines are more likely to experience them themselves. In fact, if one parent suffers from migraines, their child has a 50% chance of also developing them. This suggests that there may be a genetic component to the condition.
Environmental factors can also trigger migraines. These can include changes in weather patterns, exposure to certain chemicals or pollutants, and even sensory stimuli like bright lights or loud noises. Stress is another common trigger, with many people reporting migraines during times of high anxiety or emotional turmoil.
- Identify triggers: Keep a headache diary to track potential triggers such as certain foods, stress, lack of sleep, or environmental factors. Identifying and avoiding triggers can help prevent future migraines.
- Manage stress: Stress can contribute to migraines, so finding ways to manage and reduce stress levels can be beneficial. Techniques like relaxation exercises, meditation, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies and activities you enjoy can help.
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule: Adequate and consistent sleep is essential in managing migraines. Establish a regular sleep routine, aiming for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet: Dehydration and certain foods or additives may trigger migraines in some individuals. Drink plenty of water and consider keeping a healthy and balanced diet.
- Use relaxation techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and biofeedback techniques can help you relax and potentially alleviate migraine symptoms.
- Consider over-the-counter pain relief: Non-prescription pain medications such as acetaminophen (paracetamol), ibuprofen, or aspirin may provide relief for mild to moderate migraines. However, it’s important to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or if these medications don’t provide adequate relief.
- Prescription medications: If your migraines are severe or frequent, a healthcare professional may prescribe specific medications to help prevent or manage migraines. These may include triptans, anti-nausea medications, or preventive medications taken regularly to reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines.
Remember, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your specific situation, provide an accurate diagnosis, and offer appropriate treatment options based on your individual needs.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for individuals suffering from migraines. However, medication may not work for everyone and can have side effects.
Lifestyle changes can also be effective in managing migraines. This includes getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, reducing stress, and avoiding trigger foods. Alternative therapies like acupuncture, massage, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can also be helpful for some individuals. It’s important to discuss all options with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for each individual.
Living with Migraine
There are several different types of migraines. Here are some of the common types:
- Migraine without aura: This is the most common type of migraine. It involves moderate to severe headache pain that is usually on one side of the head, along with other symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. However, it does not have an associated aura.
- Migraine with aura: Some people experience warning signs called auras before the onset of a migraine headache. Auras are usually visual disturbances such as seeing flashing lights, zigzag lines, or temporary vision loss. Other aura symptoms may include tingling or numbness in the face or hands, difficulty speaking, or confusion.
- Chronic migraine: Chronic migraine is diagnosed when a person experiences migraines on 15 or more days per month for at least three months, with at least eight of those days being migraines with or without aura. Chronic migraines can significantly impact daily life and often require more aggressive treatment approaches.
- Hemiplegic migraine: Hemiplegic migraines are characterized by temporary paralysis or weakness on one side of the body (hemiplegia) during or after the headache phase. Other symptoms may include visual disturbances, difficulty speaking, and sensory changes. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms to rule out other conditions.
- Vestibular migraine: Vestibular migraines are associated with dizziness, vertigo (a spinning sensation), and problems with balance and coordination. People with vestibular migraines may or may not experience headache pain.
- Menstrual migraine: Some women experience migraines that are closely linked to their menstrual cycle. These migraines tend to occur in the days before, during, or after menstruation. The hormonal fluctuations during this time are believed to be a trigger.
- Retinal migraine: Retinal migraines are rare and involve temporary vision loss or blindness in one eye. The vision loss can last from minutes to an hour and is usually accompanied by a headache.
It’s important to note that the diagnosis and classification of migraines are best made by a healthcare professional based on your specific symptoms and medical history. If you experience migraines, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Living with migraine can be challenging, but it is possible to manage your symptoms and lead a fulfilling life. One of the most important things you can do is to identify your triggers. Keep a journal of your migraines and note any patterns or commonalities. This will help you avoid triggers in the future.
It’s also important to have a support system. Talk to your family and friends about your migraines and let them know how they can help. Consider joining a support group or seeking professional counseling. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, migraines are a complex neurological condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. We have learned that migraines differ from regular headaches in their symptoms and duration, and that they can be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices. While there are various treatment options available, it is important for individuals to work with their healthcare provider to find the best approach for managing their symptoms and improving their overall well-being.
Living with migraines can be challenging, but there are steps individuals can take to manage their symptoms and live a fulfilling life. This includes identifying triggers, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By taking control of their condition and seeking support from healthcare professionals and loved ones, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of migraines on their daily activities.