Introduction
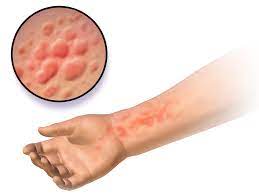
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by raised, red, itchy bumps that can appear anywhere on the body. While urticaria may seem like a minor inconvenience, it can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life.
For many individuals, living with urticaria means dealing with constant discomfort and embarrassment. The physical symptoms can be unbearable, and the emotional toll can be just as challenging. In this presentation, we will explore the causes and types of urticaria, its impact on daily life, treatment options, and ways to prevent and manage this condition.
What is Urticaria?
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, itchy welts or bumps on the skin that can appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly. These hives can range in size from small spots to large patches and can occur anywhere on the body.
There are two main types of urticaria: acute and chronic. Acute urticaria typically lasts less than six weeks and is often caused by an allergic reaction to food, medication, or insect bites. Chronic urticaria, on the other hand, lasts for more than six weeks and may be caused by an autoimmune disorder or unknown factors. Symptoms of urticaria include itching, burning, and stinging sensations, as well as swelling and redness of the affected area.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with urticaria can be a constant struggle. The unpredictable nature of the condition means that those affected never know when an outbreak will occur, making planning and scheduling difficult. The physical symptoms of urticaria, such as itching, swelling, and hives, can also be uncomfortable and distracting, making it hard to focus on work or other activities.
But perhaps even more challenging are the emotional effects of urticaria. The visible nature of the condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and embarrassment, especially if outbreaks occur in public. This can lead to social isolation and anxiety, as well as a sense of frustration and helplessness. For those with chronic urticaria, the impact on mental health can be significant, leading to depression and other mood disorders.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for urticaria, including medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
Antihistamines are the most commonly prescribed medication for urticaria. They work by blocking histamine, which causes the allergic reaction that leads to hives. However, they can cause drowsiness and other side effects in some people.
Corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe cases of urticaria, but they should only be used for short periods due to their potential side effects.
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and herbal remedies are also used to treat urticaria, but there is limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness.
Lifestyle changes such as avoiding triggers, wearing loose clothing, and using cool compresses can also help manage symptoms of urticaria.
Prevention and Management

Identifying triggers is an important step in preventing and managing urticaria. Common triggers include certain foods, medications, and environmental factors. Keeping a diary of symptoms and activities can help identify triggers.
Avoiding allergens is another key aspect of prevention and management. This may involve avoiding certain foods or substances, using hypoallergenic products, and taking precautions when outdoors.
Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can also be helpful in reducing the frequency and severity of urticaria outbreaks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have learned that urticaria is a condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life. It can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress, making it important to seek treatment and management options.
We have discussed various treatment options, including medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies. It is important to weigh the pros and cons of each option and work with a healthcare professional to find the best approach for each individual.
Prevention and management strategies such as identifying triggers, avoiding allergens, and stress management can also play an important role in managing urticaria.
Overall, it is crucial to understand and address urticaria in order to improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition. We encourage everyone to spread awareness and support those who are impacted by urticaria.