Introduction
It’s a topic that may not be top of mind for many of us, but it’s one that’s becoming increasingly important to understand.
Fatty liver is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver, which can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. With the rise of obesity and other related conditions, fatty liver has become a growing concern for healthcare professionals and individuals alike.
What is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver. It is a common condition that can be caused by various factors such as obesity, high cholesterol, and diabetes. While some fat in the liver is normal, too much fat can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver.
The symptoms of fatty liver may not be noticeable in the early stages, but as the condition progresses, symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice may occur. Fatty liver can also increase the risk of developing other health conditions such as liver cancer and cirrhosis.
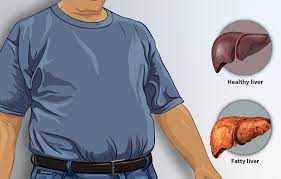
Types of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease is categorized into two main types: alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, which can lead to fat accumulation in the liver. NAFLD, on the other hand, is not related to alcohol consumption and is often associated with obesity and metabolic disorders such as diabetes and high cholesterol.
While both types of fatty liver disease share some similarities, they also have distinct differences. For example, AFLD is more likely to progress to more severe forms of liver disease, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis, while NAFLD is typically a milder form of the disease that may not progress past simple fatty liver. Visual aids can be helpful in illustrating these differences and helping the audience understand the nuances of each type of fatty liver disease.
Risk Factors
Obesity is one of the leading risk factors for fatty liver disease. When a person is overweight, their liver becomes overloaded with fat, which can lead to inflammation and scarring. In fact, studies show that up to 90% of people with obesity have some degree of fatty liver disease.
Diabetes is another major risk factor for fatty liver disease. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to the liver over time, leading to the accumulation of fat. In fact, up to 70% of people with type 2 diabetes have some degree of fatty liver disease.
Diagnosing tests:
Commonly, the diagnosis is incidental. Some tests which identify the disorder are:-
- Ultrasound (Ultrasonography): abdominal scan can measure the liver size and this test can be valuable in grading the improvement.
- Liver Function Tests: Abnormal levels of liver enzymes in the blood . This test gives the depth of derangement in functional level
- Computed Tomography Scan (CT scan): non-invasive. Measures internal organs accurately and in detail by the use of X-rays.
- MRI:
Prevention and Treatment :
To prevent fatty liver, it is important to maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is also crucial in preventing alcoholic fatty liver disease. Additionally, managing underlying medical conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol can reduce the risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
In terms of treatment, lifestyle changes are often the first line of defense. This includes losing weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol. Medications may also be prescribed to manage underlying conditions or to specifically target fatty liver. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Homeopathy:
Depending on the cause of disease and stage of the disease it can be treated. some of the most common remedies are Antimonium crudum, carduus ,chelidonium majus, lycopodium, natrum phosphoricum, nuxvomica, etc., depending on the totality of symptoms physician chooses the similimum.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fatty liver is a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and even liver failure if left untreated. However, there are steps you can take to prevent and treat fatty liver, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol and high-fat foods.
It’s important to understand the risks and symptoms of fatty liver, as well as the different types and causes. By taking action to improve your lifestyle and seek medical treatment if necessary, you can reduce your risk of developing fatty liver and improve your overall health and well-being.